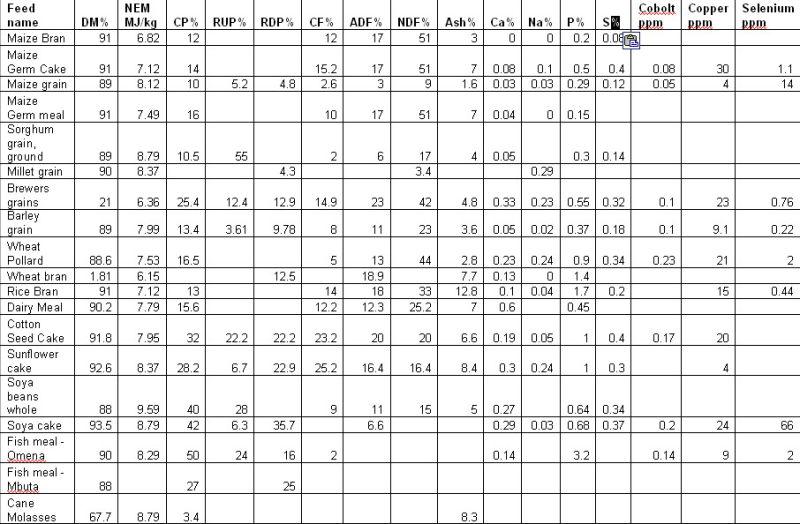
Food, Water and Equipments
“You cannot make a Holstein a Jersey,” teased Tom Jenkins during the Hoard’s Dairyman monthly webinar. Genetics plays a big role in components. We can fine-tune our rations to take advantage of a few scenarios, but there’s no management silver bullet to dramatically bolster components during the hotter months of the year.
(Dairy Vietnam) The Nutracor is a calcium soap of long chain fatty acids made from freshly processed fatty acid distillates of palm and reacted with calcium sources.
Breeding Mulato II was developed at CIAT from an original B. ruziziensis x B. decumbens cross, followed by 2 generations of hybridisation by exposure to B. brizantha pollen in the field and was released by Grupo Papalotla in 2004. In trials in Central and South America, Mulato II produced more dry season forage and had better milk production over time than Mulato and other Brachiaria cultivars..
Mineral Nutrition: Forages are typically a variable source of minerals as they are dependent on the status of the soils. Past wet seasons may have led to higher levels of leaching, resulting in an imbalance of minerals in cow diets. Some minerals may be in short supply, while others at high levels can be antagonistic to other minerals.
(Dairy Vietnam) GLOBAL - The 2012 corn crop has been under significant stress; as a result the overall quality is a concern to livestock and poultry producers. BIOMIN is hosting an educational webinar focussed on quality findings, possible effects to livestock and poultry and solution-based strategies to cope with mycotoxins.
US - All dairy producers are aware their cows are subject to heat stress on warm summer days. Experts estimate heat stress causes $5 to $6 billion in lost milk production and decreased animal performance in the United States each year, writes Craig Thomas, Michigan State University Extension.
J A H Evans, Dairy Consultant
Adding milled rapeseed to dairy rations reduced methane emissions, and reduced the saturated fatty acid (SFA) content and increased the cis-monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) content of milk, according to research from the University of Reading.
April 2012 marks the beginning of the final year of research being undertaken on four exciting grass and clover ‘Breeding LINK’ projects at the Institute of Biological, Environmental and Rural Sciences IBERS (Aberystwyth University). 'Breeding LINK' comprises four projects funded under the Defra Sustainable Livestock Production (SLP) LINK programme.
Microbial fermentation in the rumen dominates the nutrition of ruminant animals. Microbial ecosystems lend themselves to manipulation by external means, and it has long been clear that feed additives could be used to improve the nutrition of ruminants by manipulating ruminal fermentation. Ionophores and antibiotics have been used in the past to achieve some nutritional goals, however the recent ban of antimicrobial feed additives in the EU has lead to renewed interest in plants or their extracts as feed additives, with some success. This paper reviews recent progress in understanding how plants and their extracts may be used as rumen manipulating agents, with some benefits that were provided by ionophores and others that may improve the health of the animal and the healthiness of ruminant products.