World Dairy
Viet Nam: The emergence of a rapidly growing industry

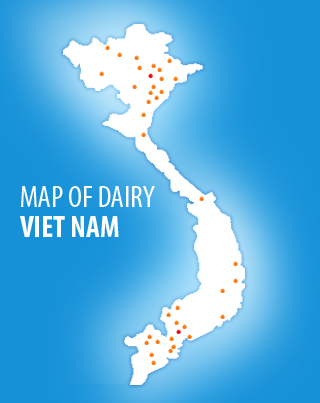
Background
- Private production, which includes small- and medium-scale producers who are mostly private farms, private domestic or joint venture companies. This system generates 95 percent of the total milk production in the country.
- State-owned farms/stations generating the remaining 5 percent of the total milk production in the country.
Trade policy in the context of WTO integration
Viet Nam protects its indigenous dairy industry with tariffs on imports of dairy products and duty quotas. According to an early International Research Centre study on the Vietnamese level of trade protection, the dairy sector enjoyed “considerable benefits from governmental interventions” with a nominal rate of protection calculated at 22.6 percent and an effective rate of protection54 at 36.6 percent ( Sullivan , 2002).
During the negotiations for Viet Nam’s membership into the World Trade Organization (WTO) and its ensuing accession in early 2007, there was considerable pressure on the Government to reduce its current import tariffs on dairy products. These tariff pressures were preceded by ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) tariff negotiations and reductions, which were agreed upon in 2005.
The main area of concern was linked to import tariffs on skim milk powder and whole milk powder. Tariff levels on other dairy products were also important, such as UHT milk and butter oil, which were products that could be produced in Viet Nam. But a lowering of the import tariffs potentially jeopardizes the ambitious plan of the Government to substitute imported dairy products with locally produced raw material. There is, therefore, a tangible risk that the Government’s plans to expand the dairy sector will not be fulfilled if the tariff rate falls below its existing level.
Exporting countries to Viet Nam are grouped into two categories:
- 1) WTO members with whom Viet Nam applies the most favoured nation (MFN) tariffs, with tariffs on manufactured dairy products currently that 30 percent, while tariffs on raw material and pre-manufactured products (among others, skim and whole powder) currently at 10–15 percent, depending on the kind of product and on its fat and sugar content.
- 2) AFTA members, for whom common effective preferential tariffs (CEPT) apply. In 2005, the CEPT tariffs for dry skim and whole milk powder were subjected to a 10 percent tariff and were reduced to 5 percent for both categories by 2006. CEPT tariffs also depend on the kind of product imported and on its fat and sugar content.
Recent trends and expected future developments in the dairy sector
High growth rates slow in recent years
Table 1: Dairy cattle and milk production, 2000–2006
|
Product |
2000 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
|
Dairy cattle (million head) |
35 |
41 |
55 |
79 |
95 |
104 |
113 |
|
Growth rate (%) |
|
17.14 |
34.15 |
43.64 |
20.25 |
9.47 |
8.72 |
|
Milk production (‘000 tonnes) |
51.4 |
64.7 |
78.4 |
126.7 |
151.3 |
197.7 |
215.9 |
|
Growth rate (%) |
|
25.88 |
21.17 |
61.61 |
19.42 |
30.67 |
9.21 |
|
Source: MARD, 2007. |
|||||||
Strong support from government and local authorities
Provincial governments also have generated dairy development policies that include provisions such as:55 free or subsidized artificial insemination and vaccine services;
- compensation of 200 000 dong per male calf born (in the first three years of a provincial dairy project);
- subsidy (2–3 million dong) for the purchase of Laisind cows for artificial insemination with the dairy breed;
- subsidy (5–7 million dong) for the purchase of exotic dairy cows;
- interest-free (1–3 years) bank loan for the purchase of dairy cows;
- support for costs for cow shed improvements;
- support for grass production costs;
- support for milk collection and transportation.
In addition, some provinces have:
- exempted taxes on agricultural land;
- prioritized land availability for fodder production.
Milk productivity is increasing steadily with an appropriate breed strategy
From 2000 to 2006, the average milk productivity of cross-bred Holstein-Friesian (HF) cattle increased from 3.8 tonnes to 4.7 tonnes (in a 305-day period; MARD, 2007). This productivity is comparatively higher than that of other countries in the region (China at 3.4 tonnes, Thailand at 3.2 tonnes, Indonesia at 3.1 tonnes).
The increase of Holstein-Friesian cross-bred cattle (through an artificial insemination programme) is considered the backbone of the NDDP and the main booster of milk production in Viet Nam. The breeding programme benefits farmers by increasing the body size and growth rate of local cattle and thus improving their productivity. The dairy breeding programme is then implemented by inseminating local improved cows with pure Holstein-Friesian bull semen to produce the cross-bred cows.
As result, 14 percent of total dairy cattle population currently is pure Holstein-Friesian cows, 85 percent is cross-bred (with a cross-bred proportion growing from 50 percent to 75 percent to 87.5 percent); only 1 percent is some other breed. Some 47 000 (41.5 percent) of the total 113 200 dairy cattle were carefully selected and recorded in the national cattle breed book, which can be accessed freely via the Internet. All the semen for inseminating is also selected from potential bulls, which can ensure greater milk productivity.
Dairy development lessons accompanied by failures in unfavourable regions
In its Decision No. 167, the Government approved only 12 provinces for participation in its dairy development plan. However, 33 provinces ended up in the final plan due to direct request from the People’s Committee in the other provinces.
In 2006, those 33 provinces maintained a dairy cattle sector. However, according to the MARD, within the first six months of 2006, the dairy cattle population decreased sharply in 12 provinces (Department of Livestock Production, 2006). The proportion of unqualified heifers increased, with calves and even milking cows left for slaughter in those provinces. In the North, cattle numbers declined in Thai Nguyen province by 45 percent, in Phu Tho by 68 percent, in Thai Binh by 37 percent, in Ha Nam by 18.5 percent; in the South, they decreased in Tra Vinh by 80 percent, in Vinh Long by 34 percent, and so on.
The decline was attributed to insufficient preparation of the dairy cows for milk production and the lack of fodder supply, due to unfavourable natural conditions or the lack of production zone planning. Pure Holstein-Friesian cows were imported but proved not so appropriate with the local climate and more difficult for farmers lacking experience than cross-bred cows. Also, many dairy farms were distant from a dairy company, a situation compounded by the lack of collection and storage facilities.
|
Box 1: Failures of dairy development plan in inappropriate provinces Tuyen Quang became the first province to announce its failure with the National Dairy Development Plan. Over a four-year period (2003–2006), the province imported 3 279 pure Holstein-Friesian cows. But by September 2006 only around 1 000 of them werealive. The loss was attributed to insufficient infrastructure, lack of efficient management and that the plan was an exercise in “central planning” rather than an economic development plan. In 2000, the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (DARD) of Son La province requested the Provincial People’s Committee to import 100 dairy cows in order to set up pilot demonstrations at potential dairy farm households. However, the People’s Committee approved a plan to import 6 000 dairy cows. The DARD later recorded that of those 6 000 cows, only 945 cows were in lactation, 222 had died and the rest could not conceive. Source: Rural Economy Newspaper, September 2006 |
Scale of production at the household level is increasing
The average number of head per dairy cattle herd is increasing, and the proportion of herds with less than five heads is decreasing. The typical herd now consists of five to ten head. Economies of scale are considered the most important reason for this change, with capital availability the biggest constraint to increasing the scale of their production, especially among the smallholders.
Dairy companies depend on imported milk powder rather than domestic fresh milk production
Import dependency has resulted in a value-chain segmentation among the milk producers, milk processors and milk consumers, each of whom have different priorities. Because domestic production meets only 22 percent of the total demand of dairy companies, international market developments influence the Vietnamese dairy sector. For instance, domestic milk powder price decreased in Viet Nam after its WTO accession in 2007. By importing milk powder to process “fresh milk”, milk companies have had greater profits than when using domestic fresh milk. And it partially explains why the price of fresh milk, which was mostly procured by the large-scale milk companies, remained constant (at least from 2002 to 2006) while the input costs rapidly increased.
On the consumption side, fresh milk supplies are not highly appreciated by Vietnamese consumers, who seem to consider the short shelf life of pasteurized milk as an indication of inferior quality. In addition, the low prevalence of home refrigeration, especially in rural areas, makes UHT milk more convenient for consumers. However, as average income increases in Viet Nam, processors are expecting some shift of consumption habits, from UHT milk to pasteurized milk. Changes in habits are helped along by marketing and improving awareness on the quality of pasteurized milk in contrast to UHT milk, as Nestlé has discovered.
World price increases translate to opportunity for Viet Nam dairy farmers
From June 2007, two of the main dairy companies, VINAMILK and Dutch Lady, increased the farmgate price from 4 600 dong per kg to, first, 5 000 dong per kg and then to 6 400–6 800 dong per kg at the end of June 2007. The world demand for milk in 2007 increased sharply (by 35–100 percent), pushing up prices, particularly in a context of drought and reduced-fodder availability. Additionally, some European Union countries cut the subsidies in the dairy sector, making the milk price rise closer to the real value of products.
This is a real opportunity for dairy farmers in Viet Nam. The price gives farmers a profit of 3 000–3 500 dong per kg, or 45 000–52 000 dong per day ($2.8–$3.25 per day) for 15 kg of average daily yield per dairy cow, a very valuable income for rural households. The cost of dairy calves also has decreased, from 24 million dong per head (as a result of the high demand at the peak period of the NDDP) to 17–19 million dong per head (considered the “real” price of a calf).
Figure 1: Milk flow and dairy price charts

Smallholder farmers move into dairy production
Success of the NDDP and other support programmes/projects
|
Box 2: A smallholder farmer finds success in Dong Nai province Like many other farmers in Long Thanh, Dong Nai province, Lam Quang Tri lived a hard life cultivating primarily cashews and rice, although he owned some goats and sold their milk. In 1982 he recognized that the goat milk was limited, with one goat producing only 1 litre of milk a day. So he looked into dairying, in which one cow produces 10 litres of milk a day. He sold the family’s jewelry and borrowed from relatives to buy six Sind cows. He then set aside 1 ha (most of his land at that time) for planting grass as feed for his cows. Each time a cow became sick, he turned to a veterinary technician at the An Phuoc Cow Factory for help. Eventually he began reading books on cattle husbandry and found ways to treat his cows on his own. Although he also sought out professors at the Agricultural University and the Southern Institute of Agricultural Science on disease treatment, raising techniques and cow-development methods. In 1985, his cows began producing milk. At first he tried selling it locally, but people were not familiar with such fresh cow’s milk. He then learned how to treat it by cooking it in a two-layer bain-marie and then distiling it into clean glass bottles. The locals were still reluctant to even try it. So he made yogurt and offered it plus the milk for free, at least to people he knew. The approach worked, and after just a short time, his customer base increased quickly. His sterile fresh milk is now famous in the region. In 2003, Mr Lam Quang Tri’s herd grew to more than 100 cows and his grassland expanded to 5 ha. He signed a contract to sell a portion of his milk to the An Phuoc Milk Company, which sells processed milk to VINAMILK. Mr Lam Quang Tri ’s success is largely a tribute to his creativeness and responsiveness to the market. That he achieved a stability of input from his own grass and feed provided through contracts with a local animal feed company also helped. And the technical and extension agents he sought out at scientific institutions also played a crucial role. However, in 2004 the farmer encountered several difficulties, especially increased prices for feed, labour and transportation and decreased milk prices. This led to a reduction of his herd to 80 cows and a loss of revenue by 30–35 percent. |
|
Box 3: Dairy development plan implemented in many provinces After the declaration of Government Decision No. 167, the Thai Nguyen provincial leader initiated a dairy development production project in October 2003, with an investment of 21 billion dong. The project provides a household with 4 million dong to buy an exotic breed of cattle or 3 millions dong for a domestic breed, 200 000 dong for each male calf and 70 000 dong for each 360 sq m of grassland for feeding the herd. This plan proved to be a good incentive to shift farmers in Thai Nguyen from a solely crop production to one that includes dairy cattle husbandry. |
|
Box 4: An integrating farm success with CIDA support Seven years ago, Lieu Van Do and his family, members of the Kho Me ethnic minority in Soc Trang province, had a tough life with poor living standards despite their hard work on 1.5 ha of paddy field. In 2002, Mr Lieu Van Do participated in the a programme called Improving Rural Household Living Standards that was funded by the Canadian International Development Agency. The family received a dairy cow and training in breeding experiences from a dairy production model developed in Binh Duong . Five years later, the family’s herd had grown to seven cows. In 2006, two of their cows produced 3.5 tonnes of milk in a ten-month period, netting them more than 20 million dong in profit. Two more cows are of breeding age and will likely milk soon. The family built a new house and Mr Liew Van Do is looking to expand his herd. |
|
Box 5: Dutch Lady Viet Nam’s payment system According to 2005 information from Dutch Lady Viet Nam (DLV), the company has an elaborate but transparent pricing system, based on strict quality standards and results: minimal standards are 3.5 percent fat, 12 percent total solids and a 4 Rezasurin grade on a scale of 6 as the top quality. (In 2004, records indicate that the DLV had an overall quality rating of 3.8 percent fat, 12.3 percent total solids and a 4.1 Rezasurin grade.) DLV operates various quality check-ups, the first at the collection point and the other at the milk-chilling centre. If milk is rejected at the milk collection centre, it is returned to the collection point so that other farmers do not have to bear the responsibility for bad quality. Milk payment is made every 15 days and based on the daily average results of the collection points and on random individual quality checks (one per payment period). If individual farmers have a lower quality than the group’s average, they are penalized; if they have a higher quality, they are rewarded. Specialized farmers receive individual payment. In 2005, DLV developed a software program for making its payments. Results from weighing and quality checks are registered; farmers receive a payslip that they can check against their own production records. Upon presentation of their bi-monthly payslip, farmers receive payment from the bank. |
|
Box 6: A struggling dairy development plan in Thai Nguyen province Despite favourable policies and intervention mechanisms, two years after the Thai Nguyen provincial government began its support, the total dairy herd in the province attained only 20 percent of the planned targets. In that time, the government had distributed only 491 milk cows and 816 million dong subsidies to 199 households and enterprises. Among them, only 74 milk cows could be milked (accounting for 9 percent of the planned target). The dairy herd did not increase, leading to a reduction in grassland each year (although grassland can double in profit compared with the same area for farm production). In 2003, a total of 147 ha was planted as grass feed; only 82 ha was plannted a year later but then dropping to 9.7 ha in 2005. There are many reasons for this failure in dairy development. The most obvious one is that a comprehensive market study was not completed initially. Also, Thai Nguyen developed the dairy sector too fast, mostly as a movement – creating a “herd-effect” kind of activity. In fact, when the project was implemented, almost every Thai Nguyen farmer did not understand that raising dairy cows is very different from raising other livestock. Even the authorities could not imagine the overall picture of the sector to properly prepare for it. In addition, the quality of breeding animals was not well chosen. To meet the demand for breeding, many agencies and enterprises hastily imported cow breeds, many of which were of good quality but not suitable to the region. Breeding dairy cows requires considerable investment, with much more time needed to recoup costs and an output market difficult to control. Because of this, many farmers believed that the work was less profitable than expected, and thus gave up and sold their cows. An yet, initially they felt highly enthusiastic; they borrowed money to build facilities, to buy breeding animals, to shift to grass cultivation, to grow or purchase maize for feeding. Now, the “dream” of making money from raising dairy cows has disappeared, replaced by anxiety over selling produce and repaying the debts. |
|
Box 7: An unsuccessful contract in Thai Nguyen Thai Nguyen provincial authorities expected dairy companies and farmers to sign contracts. Based on the contracts, a company would provide investment for milk-storage systems, facilitating the preservation of milk for purchase. However, up to now, there are no signed contracts. A company only invests when it is ensured that the farmers will provide enough milk for their production needs. Generally, one milk storage facility can hold at least 2 000 litres of milk a day. However, the current production level only fills 15–20 percent of that capacity. But many famers have been waiting for a company to sign a contract before buying their dairy cows. This circle of reluctance has considerably impeded the project’s progression. |
|
Box 8: Contract farming with Nestlé in Ha Tay province In 1998, Nestlé cooperated with the Ha Tay People’s Committee to encourage farmers to convert from rice growing to cow raising. With careful training, technology subsidies and inexpensive credit, many farmers made the switch and signed annual contracts with Nestlé. The company also provided other facilities, such as milk-collection terminals, complementary equipment and cleaning chemicals. By 2004, Nestlé was collecting 93 percent of the milk. Under the contract, Nestlé buys milk from groups of farmers, and, in return, the group is obliged to sell all their milk to Nestlé. The farmers are responsible for building up their farms and paying for most inputs, such as feed, electricity, water and labour. Prices, which are determined solely by Nestlé, barely reflect the market price. However, Nestlé wants to ensure a stable price throughout the year under the contract, even if prices harshly fluctuate across a year. Nestlé has a bonus and fine system to control the milk quality. Random samples of milk from each village are tested every month. Among the different issues, Nestlé is most careful about the proportion of antibiotic, which is only allowed to be less than one-billionth. To achieve such a small proportion, Nestlé trained the farmers and provided a gradual scale of qualifications. The Nestlé contract system has produced a variety of experiences:
The low prices resulted not only in a lower quality but also a lower quantity of milk; the amount of milk produced by each dairy cow decreased to only 10–12 kg per day, compared to 18–20 kg per day in the 2004–2005 period. Deep in the milk-price crisis, the farmers were trapped in a frustrating cycle in which a small income from milk provides insufficient nutrition for the cows. The cows, in return, provide low milk quality and quantity, thus producers earn even less money. Many of contracted farmers coped with the crisis by slaughtering the cows that didn’t provide enough milk and changed to other businesses. Nestlé offered no solution for the contract violations. There was no legal system that the company could rely on nor could it bind the farmers economically. Further, there was little threat of the company’s refusal to renew the contract because it lacked milk and needed as much milk as it could obtain. The company now has resorted to powdered milk as an alternative input for production. As an attempt to target the problem of reduced milk quantity, Nestlé decided to buy milk by cluster. Each cluster had a leader, elected by the members, and then trained by the company. The cluster leader ensure that the farmers supply the contracted amount of milk and distribute the company’s payment to everyone. In an attempt to strengthen the contract system, Nestlé offered the leader a fixed salary and payment for his/her electricity bill. As more farmers started to break the contract arrangements, the company decided to award the cluster leader with 200 dong for each kg of milk collected to increase his/her incentive. Buying milk by cluster also helps Nestlé better control the quality of the milk because the milk from many households is now stored in one container. If one household has antibiotic in the milk, it will affect others economically and lead to social costs. The households will, hence, monitor one another to ensure mutual benefit. Unfortunately, having the cluster leader as the mediator has caused occasional conflicts within each cluster. Even though he/she was elected by the farmers, the leader is sometimes non-transparent in distributing payments. For example, a leader might receive payment from the company but delay the distribution. The company has yet to find a way to tackle this conflict. At the end of 2006, the rate of contract violations, estimated by the company’s business director, was approximately 50 percent, though the real rate could actually be higher. |
Prospects
- The National Dairy Development Plan and subsequently Decision No. 167 (amended), concentrated technical and financial efforts in the “dairy priority zones”, identified in a manner similar to what has been used for priority “economic zones”. However, the criteria for such zones should be: i) a tradition in dairying, ii) an existing level of technical know-how, iii) availability of processing facilities and current access to markets, iv) climate and natural constraints/strengths, v) land availability for fodder cultivation and vi) availability of industry by-products.
- Smallholders tend to disappear from dairy production in crisis periods. Typically, smallholders are more vulnerable because they are relatively new to dairying and did not have enough time to gather sufficient resources to pay back their debts and enlarge their herd.
- All efforts should be made to strengthen the capacity of existing small- and medium-scale farmers who show a potential to enlarge their herd (enough land, interest, technical know-how) smallholders should, whenever possible, be encouraged into interest groups in order to lower their production costs. The organizational approach should be addressed step by step (primarily by forming interest groups or clubs rather than cooperatives). Active exchange of experiences should be promoted by study tours to private farms and existing interest groups.
- Developing very large farms with the latest technology might, at this stage, not be sustainable in Viet Nam. Large estates should not be artificially created by the central or provincial governments (exceptions might be joint ventures, drawing foreign capital and technical inputs) but should naturally evolve from existing large private structures.
- To resolve limitations imposed by farmers’ lack of dairy experience, extension agents and veterinary staff, it is necessary to have financial and technical efforts to tackle the human resources constraint. Technical staff with existing knowledge in dairy (veterinarians, extension agents) should be used as trainers in the areas identified as priority dairy zones. Extension agents in priority dairy zones should be specifically trained on dairy issues, not only on theoretical matters but on practical topics (hand milking, feeding, heat detection, deliveries, management of animals, etc.).
- In each zone, successful farmers with sound technical knowledge should be identified as possible farmer-to-farmer trainers. Farmers should be intensively trained on relevant topics (heat detection, calf raising, feeding, hygienic milking, basic detection of health disorders, etc.), possibly on their farm rather than at a station (exchange of experience with successful farmers).
- Regarding the situation of breeding policy and breed selection, Viet Nam should emphasize improving the management of the various types rather than on the appropriate level of exotic blood.
- For feed and fodder availability, significant efforts are needed to establish “priority fodder-growing areas” in communes with dairy production. Villages, communes and districts of priority dairy zones should elaborate a plan for fodder-growing suitable to existing conditions (Taking into account irrigation facilities and constraints, seasonality and land quality).
- Smallholder farmers should be encouraged to buy feed, industrial by-products (brewery waste) and crop residues (rice straw) in bulk to short-cut several layers of middlemen. This can be achieved by encouraging farmers to form interest groups or clubs (rather than cooperatives, which often have a negative connotation).
- To give more incentives for the smallholder dairy farmers, a new pricing system should be set up, based on a basic milk quality (fat, protein, total solid, bacterial count and absence of antibiotics). The basic payment system should be similar throughout the country, with private processors free to establish their own payment schemes.
- To overcome higher prices for bad quality paid by private agents and middlemen, a quality-based payment system should be implemented, similar to the Dutch Lady system: The higher the quality, the higher the price.
- At present, the economic viability and the competitiveness of Viet Nam’s dairy sector is biased by the factor of “heifer sales”. The purchase of cross-bred heifers or cows should not be subsidized or encouraged by loans or other incentives. The raising costs of heifers should be assessed on a large scale, depending on the production area (urban, peri-urban and rural). Ideally, the sales price of heifers should cover the raising costs and allow for a reasonable margin.
- To reduce the initial investment costs, farmers should be encouraged to produce their own cross-bred progenies, knowing that they run the risk of producing male calves and that dairy production takes more time to develop.
- Proper guidelines on contract conditions (such as no firm binding of dairy production and land use rights) should be issued by the national authorities. Contract dairy farming should be discussed with the major processors and the relevant ministries in order to create a general framework.
|
Box 9: Key definitions Smallholder dairy farmer: Someone who has one to three cross-bred cows, typically occupies less than 0.5 ha of land and represents the less-commercially managed dairy systems in the area. Smallholder milk producer: A smallholder dairy farmer is also a smallholder milk producer. The family consumes 8 percent of the milk produced; the surplus is sold to the local milk collection centre. The main source of income is own-farm employment (dairy and cash crops). Formal markets: Dairy companies that operate the processing facility in a dairy zone (such as collection centres set up at the commune level) and typically buy their milk either directly from farmers or via a middleman. Informal markets: Milk sellers and buyers in a neighbourhood or village. It includes smallholder dairy farmers and smallholder milk producers who sell some of their farm produce to the local market. Dairy value chain: The various stages through which milk and milk products pass from farm to the final consumer. |
Ly, Le Viet. 2006. Helping dairy farmers before too late. Bac Ninh newspaper 6/9/2006.