Breeds of Dairy cows
Project: Background - Methodology - Activities - hievement - Programs

1.Back ground
The most important points are briefly mentioned as bellow.
ã The socio-economic factors and the human demands change continuously. Before 1970, many animal breeds were used to fit the extensive animal production system. Since 1970 industrialization and specialization in animal production resulted in extinction and degradation of indigenous breeds. From 1990 onwards, the countries having advanced technologies create new breeds by crossbreeding between different genetic resources. But at present the developed and even developing countries tend to use the ordinary synthesied breeds than breeds made by gene technologies.
ã Objectives of genetic conservation: To maintain biodiversity so that create various options for animal producer to insure sustainable development and food security.
ã There1500 of the 4500 livestock breeds (FAO) are at risk of extinction and it happens mainly in developing countries.
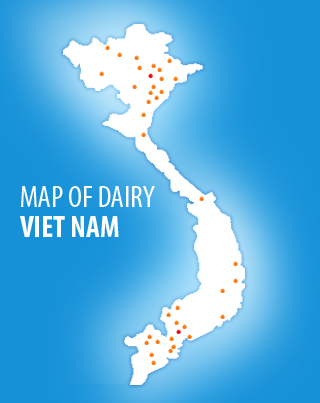
ã Vietnam is one of some countries having abundant livestock breeds. It has been known 46 local breeds. Good characteristics of the indigenous breeds are high resistance to diseases, good utilization of poor quality feed, tasty meat, good adaptability to various environment. Among these 16 breeds are present widely use in mass production, 2 breeds have loosed, 3 breeds are in danger and 25 breeds are decreased.
ã At present there are more than 30 projects for "conservation of genetic resources" being carried out since 1980. The Convention of Biological Diversity have been set up.
ã Many plans, policies and actions have been undertaken by Government of Vietnam to maintain the diversity of farm animal genetic resources. Since 1990 The National Institute of Animal Husbandry has conducted long term project "VLGRC" funded by Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment. During period of 1993-1997, a five year project "Conservation and use of animal genetic resources in Asia Pacific" was implemented with financial support from Government of Japan (GCP/RAS/144/JPN).
To protect critical breeds
To ensure existence of standardized breeds (population size, number of breeding females and males).
To develop potential breeds that are conserved subjects so as meeting consumer demands.
To provide breeds for crossbreeding with exotic breeds in order to create new products.
To establish a systematic conservation of genetic materials: semen, embryo..
To census, survey existing breeds and exploit unknown breeds for establishment information system.
Internal and external information exchange
3. The environment in which the project was implemented
Limiting budgets: 150 millions VND per year on average. (5 millions VND in 1990, 450 millions VND in 1999, JCP/RAS/144/JPN project: 100 millions VND).
That budgets must be shared to conservation, study all 46 livestock breeds
There were many activities must be taken nearly in same time: conservation live animal and genetic materials, survey, building information system.
Project was involved to many locations located from north to south Vietnam.
Project was involved to different livestock owners: farmers and people living in mountainous areas. A significant limit is the lack of knowledge in animal production.
4. Organization
Directory board:
Head Dr Le Viet Ly, Deputy of National Institute of Animal Husbandry (NIAH)
Secretary: Dr Le Minh Sat, NIAH (1990-1998),
Secretary: Dr Vo Van Su- Head for Rare Animal & Biodiversity, NIAH (from 1999)
Supervisors:
NIAH,
Department of Scientific- technology & Product quality, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD)
Department of Agricultural Scientific- technology, Ministry of Scientific - Technology & Environment (MOSTE)
Root network:
NIAH and others (See list)
5. Methods selected to realize the project
To keep animal in original habitat: putting financial, technical support for organizations, households managing the animals.
To keep animal at University, Research Institute.
Increase size of the breeds having market potential.
Cooperate with other projects inside and outside Vietnam to establish step by step conservation system of genetic materials.
On the other side, building Biodiversity information system and publishing documents.
To rescue some breeds were threatened of extinction such as: I pig in Thanh Hoa (population size now are increasing in number, about 30 pigs), Ho chicken (200 chicken). 20 other livestock breeds are given in protection network.
Some breeds had been recovered and developed to supply market demand: sheep (herdsize was increased from 1000 to 45000 in Phan rang, this breed also brought to north and ), sheep (Bachthao goat was brought from South Vietnam to North Vietnam and its herd size was increased to thousand). This contributed to increasing farmer, income for millions people living in Phan Rang, Nghe An, Ha Tinh provinces and Northern mountainous areas. Mongcai pig which was endanger now is taking important role in pig production in many households who apply half intensive production system. Ac chicken are now developing sharply in number in Northern market. About 12000 Ac chicken capitals are consumed per year. Phan Rang sheep as a new product are contributed to northern market, too.
Investing to create new products having both high productivity and high quality by crossbreeding between exotic and indigenous breeds. (for example, Dong Tao x Tam Hoang chicken, Mia x Kabir chicken, Co x Bau duck)
New genetic resources have been found: Phan rang sheep, U dau riu cattle, Meo cattle, Mini pig, H mong chicken..
Ex-situ conservation system has been established: semen, oocytes, embryos.
A data base for 70 breeds in Vietnam following FAO standard has been built. Stated studying on DNA polymorphism of growth gene, estrogen, casein.
It has been built a conservation network and conservation policies.
7. Problems unsolved
Because initiation of conservation program is late, some breeds have been loosed: Son vi pig, Van Phu chicken. Some other breeds are decreased in number: I pig, Te chicken.
Limiting budget results in population size have not reached FAO standard yet (1000 breeding females, 20 breeding males)
Breeding systems standardized by FAO have not been organized except Ac chicken.
Some market potential breeds like Phanrang goat in North, H, Mong chicken, OKE chicken have not got chance to develop in mass.
Facilities and knowledge to conserve ex-situ genetic materials have not equipped enough.
Plot farm for saving endangered breeds or researching development and demonstration have not been built.
A scientific servey on all Vietnam local breeds in order to understand them properly has not done yet.
Conservation and use of indigenous animal breeds should been done simitanously.
Establishing a system from officials to grassroots level
Standardize and modernize this work
9. Aims in period of 2000 - 2005
Increasing the number of each breed up to 20 breeding males , 1000 breeding females
Applying breeding technologies in small population in order to ensure the diversity, typical breeding characteristics and avoid inbreeding.
Conserving semen, oocytes, embryos
Exploiting unknown breeds.
Transforming market potential breeds in to production
Creating new breeds having high quality
Studying both quantity and quality traits.
Publishing Domestic Animal Diversity Information System (DADIS) on Internet standardized by FAO
Establishing conservation network from officials to grassroots, building centers keeping endangered breeds. Other breeds are kept for collecting semen, embryo or for deep researches, for demonstration. A modern laboratory is needed to equipped for molecular genetic research.
Ha noi - 25/03/2000
List units which realized the project
(Upto end 1999)
Rare animal and biodiversity Department, NIAH
Genetic and Breeding Department, NIAH
Dept. of Animal AI & Reproduction, NIAH
Dept. of Embryo Transfer, NIAH
Dept. of Cattle Science, NIAH
Dept. of Buffalo Science, NIAH
Dept. for livestock prod. system & Tech. transfer, NIAH
Ba vi Cattle Forage Res. Center, NIAH
Mountain Areas Animal Res. & Dev. Center
HoChiMinh City Livestock Res.- Tech. transfer Center
Dai xuyen Duck Res. Center
Van phuc Poultry Res. Center
Tay nguyen Univ.
Hue Agr. and Forest Univ.
Ha noi Agr. and Forest Univ.
Hong duc Univ.
Biological technology Res. Inst.
Hai hung Rice Res. Inst.
Nghe an Province Science - Tech - Environment Center
Tay bac Region Science - Production Center
Ha giang province Agr. Dept.
Ninh thuan province Science - Tech - Environment Dept
Lao cai province Agr. Dept.
Huong son district Agr. Div. for Ha tinh
Dong cao Village (Hai hung province)
Bai vi Frozen Semen Company
Thanh hoa province Lady Union
Thuan thanh District's Old people Association
Thanh to (Hai phong) Pig Farm
Trang bach (Quang ninh) Mong cai pig farm